Artificial intelligence, or AI, has been proven to be a double-edged sword, offering both benefits and drawbacks. On the one hand, AI has transformed cybersecurity, helping organizations address the cybersecurity skills gap and achieve AI-powered data security, identity and access management (IAM), AI cybersecurity threat detection and response, cloud security, and IT management.
On the other hand, the impact of AI on cybersecurity is significant. AI introduces new risks and significantly expands the attack surface. Cybercriminals leverage AI cybersecurity threats and attacks to circumvent an organization’s controls and achieve their malicious goals.
According to Accenture’s 2025 State of Cybersecurity Resilience, only 36% of security professionals acknowledge that AI is outpacing their security capabilities. However, 90% of businesses are not adequately prepared to address today’s AI-driven cybersecurity threats.
In this article, we will delve into the impact of AI on cybersecurity, common types of AI-driven cybersecurity threats, generative AI cybersecurity risks, frameworks & approaches to reduce cybersecurity risks, and how Digital Forensics Corp. helps you prevent and investigate AI cyber threats.
Understanding the Impact of AI on Cybersecurity
The advent of AI is one of the most significant advancements of the 21st century, impacting industries ranging from automotive systems to healthcare diagnostics and voice assistants. Businesses are increasingly adopting AI.
The Accenture State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2025 report notes that executives are recognizing the value of generative AI. Of these, 83% acknowledge greater business potential for this technology.
Figure 1: Estimated AI Adoption (Source: Accenture State of Cybersecurity Resilience 2025)
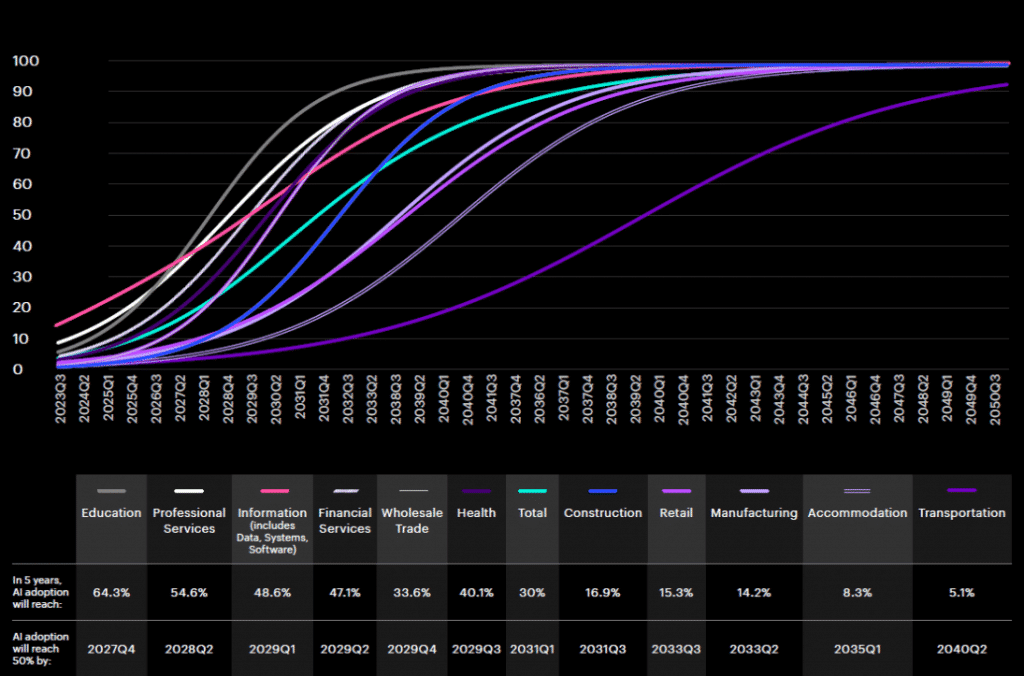
Despite AI’s transformative role in technology and cybersecurity, governments and businesses cannot ignore its dark side.
AI-powered cybersecurity threats are growing both in frequency and sophistication. Cyber pests use AI to craft modern threats and attacks, enabling hackers to remain undetected for months or even years within the victim organization’s networks or systems.
Threat actors utilize AI to automate and scale their attacks, making them harder to detect, more convincing, and faster. These attacks are difficult to detect with traditional security controls. Attackers can manage conversations, draft lures, summarize stolen data, and coordinate multi-step playbooks without relying too heavily on human effort.
Moreover, AI enables adversaries to refine their strategies in real time and become more productive. For instance, machine learning (ML) algorithms can analyze an enterprise’s defense and adapt attack methods to exploit vulnerabilities.
Neither individuals, businesses, nor organizations are free from AI cybersecurity risks. Anyone could be on the verge of a data breach. A successful AI attack can pose financial, compliance, and reputational damage to your organization.
Figure 2: The Triage of AI Impacts on Cybersecurity (Source – World Economic Forum)
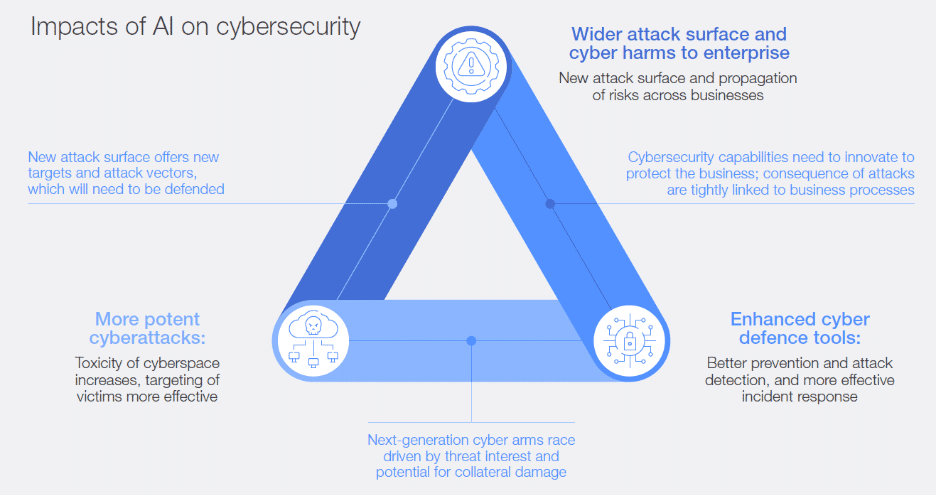
Common Types of AI-Driven Cybersecurity Threats
AI cybersecurity threats statistics are frequently making headlines. At the 2025 RSA Conference, where approximately 44,000 technology and cybersecurity experts were convened, it was revealed that AI was rapidly reshaping the cybersecurity landscape, bringing both significant challenges and unprecedented opportunities. The AI cybersecurity threats organizations face today present a serious challenge.
AI-powered threat actors can create highly convincing phishing emails, deepfake content (e.g., images, audio, video), and malicious websites to inject infected code or prompts. These methods help them craft realistic, personalized messages that are difficult to detect with traditional methods.
The threat landscape is continually broadening due to AI-powered, adaptive, automated, and targeted cyberattacks. MITRE has now established the MITRE ATLAS framework to document and analyze AI-driven cyber threats. ATLAS is an extension of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
The World Economic Forum’s Global Risk Report 2024 ranked AI-generated disinformation and misinformation as the second most severe global risk in 2024 and shows it rising to the number-one spot over the next two years. The following sections will provide insight into the common types of AI-driven cybersecurity threats and attacks.
Deepfake-Based Fraud and Misinformation
A deepfake is an audio, video, or photo that appears real but has been manipulated with AI. This AI-enabled attack can replace or swap faces, mimic facial expressions, and synthesize speech.
In fact, a deepfake can depict an individual, executive, business leader, or politician doing or saying something they never did or said.
The term was originally coined by a Reddit user in 2017. However, Henry Ajder — the head of threat intelligence at deepfake detection company Deeptrace — defines deepfakes as “synthetic media applications” that existed before the Reddit page.
In many cases, deepfakes can create a voice that mimics your boss or corporate executives on the other end of a telephone line. A deepfake video falsely depicting Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg boasting access to billions of users’ data has brought into question his platforms’ policies on fake videos.
Deepfake technology works through generative adversarial networks (GANs), which consist of two algorithms: generators and discriminators. The generators create a synthetic training data set of fake content, while the discriminators assess and refine the set for realism.
AI-Generated Phishing Campaigns
Impersonation attacks, such as phishing, are growing exponentially. Phishing is a malicious attempt to trick users into revealing private data or downloading malware. The data may include login credentials, credit card information, employees’ personally identifiable information (PII), banking details, etc.
Phishers can attack victims through phone calls, text messages, and, most commonly, email. These scammers disguise themselves as a trusted authority and mimic the real company through deceptive practices.
Scammers leverage AI and ML techniques to make their phishing attacks more convincing and faster. They use generative AI models to generate phishing emails. AI-equipped phishing scams are grammatically correct and translated into the victim’s local language, unlike past phishing attacks that were often riddled with human error.
Generative AI cybersecurity risks are increasing. In fact, approximately 30% of Iranian APT groups used an AI model, such as Google Gemini, to respond to prompts and craft material for phishing scams, according to Google Threat Intelligence Group (GTIG)’s report, Adversarial Misuse of Generative AI.
Fraudsters employ generative AI and natural language processing (NLP), a subfield of AI and computer science, to create phishing emails. Generative AI cybersecurity threats are difficult to detect with traditional security methods. Gartner believes that generative AI will trigger 17% of cyberattacks by 2027.
Machine-Learning Data Poisoning
Machine-learning data poisoning is a malicious activity in which attackers manipulate a machine learning model’s output by altering its training data. It aims to get the model to generate dangerous or biased results during “inference.” The ML model uses inference to draw conclusions from new data.
Data poisoning works by intentionally introducing bias into the training data, thereby altering the ML model’s algorithmic starting point. As a result, the ML model’s output differs from what its developers intended.
Moreover, ML data poisoning has several types, including availability attacks, data injection and manipulation, mislabeling, and backdoor poisoning.
The Open Worldwide Application Security Project (OWASP) lists AI or ML-based data poisoning in the OWASP Top 10 Risks for LLMs. In recent years, AI data poisoning vulnerabilities have affected healthcare, text generation, and code generation models.
AI Malware Adaptation
AI-generated malware uses machine learning algorithms to autonomously adapt and improve its performance, thereby remaining undetected. AI-generated malware can adjust its attack vector and execute decisions in real-time.
Furthermore, AI malware exhibits several characteristics, including real-time adaptation, obfuscation techniques, impersonation, and polymorphism.
Impersonation methods work by accurately mimicking existing attackers and known malware. On the other hand, polymorphism automatically alters its code with each infection.
Traditional signature-based methods are unable to detect or fix this malware because of its continuous mutation. Obfuscation is achieved through encryption, insertion of dead code, and substitution of instructions in the codebase.
Frameworks and Approaches to Reduce AI Cybersecurity Risks
Businesses leading in AI innovation may face risks when using new technologies that introduce undiscovered vulnerabilities.
AI-related cybersecurity threats can be greater in an organization where autonomous AI drives business processes without human oversight. Security professionals can limit risk propagation with strong human training and oversight. In addition, an advanced AI cybersecurity threats framework can play a crucial role in preventing AI cybersecurity risks.
Building an Adaptive AI Compliance and Risk Framework
As AI is evolving rapidly, its related regulatory standards and frameworks are also being introduced at lightning speed. Therefore, enterprises should adopt forward-looking, flexible strategies for AI-powered security or approaches to reduce AI cybersecurity risks.
To this end, organizations must build an adaptive AI security framework. It should not only meet regulatory requirements but also continuously evolve to address emerging cyber threats, including prompt injection, AI-driven phishing, data poisoning, and deepfakes.
In addition to compliance controls and transparent governance, enterprises should also establish and define AI-specific policies for access controls, data security, and privacy.
Integrate AI Risk Assessment
Organizations can identify vulnerabilities early by integrating AI risk assessment into product development, vendor management, and procurement.
To this end, an adaptive, real-time strategy can effectively boost security, ensure cyber resilience, and enable innovation in an ever-changing threat and compliance landscape.
Address Cloud Misconfiguration
Cloud misconfiguration is one of the most significant risks to AI security. To address this issue, cloud businesses should adopt Infrastructure as Code (IaC). It ensures that security is built into the cloud environment by default, reducing human error and eliminating misconfigurations.
Moreover, cloud security professionals should integrate security into cloud operations from the outset. It will embed tools directly into cloud application teams and DevSecOps workflows.
Integrating security into cloud operations enables real-time policy enforcement, continuous monitoring, and automated AI threat detection systems. These security controls help security professionals detect vulnerabilities in time before they become a major nightmare.
Team and Employee Training
Continuous learning plays a significant role in maintaining agility. Therefore, businesses must provide teams and employees with regular AI risk management training. It will help them anticipate and respond to AI-driven attacks promptly.
Moreover, businesses should assign explicit oversight roles to address new challenges and prevent ethical issues, AI-specific risks, and data breaches. They should also regularly update AI best practices based on regulatory feedback, internal audits, and lessons learned from real-world cyberattacks.
Empower Human Risk Awareness
Technology advancement won’t address AI risks alone. Instead, humans are always in the first line of defense in any thriving cybersecurity ecosystem. AI-driven phishing, deepfakes, and identity fraud are playing havoc with human psychology and circumventing traditional security controls.
More importantly, AI-focused security awareness training is essential. Hence, senior leaders, employees, frontline staff, executives, developers, and all other stakeholders should be able to understand AI risks relevant to their responsibilities. AI-specific security awareness, including phishing simulations and hands-on incident response drills, will ensure cyber readiness in the face of AI-driven threats.
How Digital Forensics Corp. Helps You Prevent and Investigate AI Cyber Threats
Digital Forensics Corp. is your trustworthy, reliable cybersecurity partner, helping you survive and thrive in the competitive cybersecurity and AI industry. We can empower your corporate systems and networks with world-class AI-powered threat detection and response.
Our highly skilled forensic experts can effectively perform AI-enabled threat analysis, malware tracing, phishing detection, and system recovery. In addition, DFC provides you with consulting, investigation, and defense services for AI-driven threats and attacks.
If your organization suspects AI-based cyber threats, contact Digital Forensics Corp. for professional forensic support.
FAQ – AI Cybersecurity Threats and Risks
What are the latest AI cybersecurity threats?
There are several latest AI cybersecurity threats, including deepfakes-based fraud and misinformation, AI-based malware, machine learning-based data poisoning, and AI-enabled phishing campaigns.
How can AI be used in cyberattacks?
AI can be used to generate cyberattacks. For example, cybercriminals can employ ChatGPT, Gemini, Copilot, or Claude to create phishing emails. AI-equipped phishing scams are grammatically correct and translated into the victim’s local language.
What is generative AI cybersecurity?
Generative AI can streamline cybersecurity by automating routine security tasks, such as scanning for vulnerabilities, configuring firewalls, and using AI for cybersecurity threat detection. It will save time for human security experts and help them pay heed to other essential activities, such as decision-making. Contrarily, generative AI cybersecurity threats are also common.
How can companies detect AI-driven attacks?
Companies can detect AI-driven attacks by leveraging AI-driven security tools and best practices in their Security Operation Centers (SOCs).
Is AI in cybersecurity safe for organizations?
Despite AI’s transformative role in technology and cybersecurity, governments and businesses cannot ignore its dark side. AI-powered cybersecurity threats are growing both in frequency and sophistication. The risks of AI in cybersecurity are significant.






